What is professional services automation (PSA)?
Professional services automation (PSA) is a type of software application suite that provides a service business with the functionality it needs to manage core business processes. PSA software provides essential business automation for professional services organizations, such as law firms and accounting partnerships.
PSA tools play a role similar to that of enterprise resource planning (ERP) software products and other management tools in industries such as manufacturing and retail. In the IT industry, consulting firms and managed service providers (MSPs) use professional services automation software to help run their day-to-day operations. PSA systems can help organizations with project planning, on-time project delivery, project performance, revenue recognition and operational efficiency.
What PSA software does
PSA software integrates various business functions into a single technology, replacing the need for separate tools for resource planning, billing, time tracking and project management. By managing the entire lifecycle of a project from initial sales opportunity through sales motion, invoicing and reporting, PSA software provides a streamlined, consistent approach to service delivery.
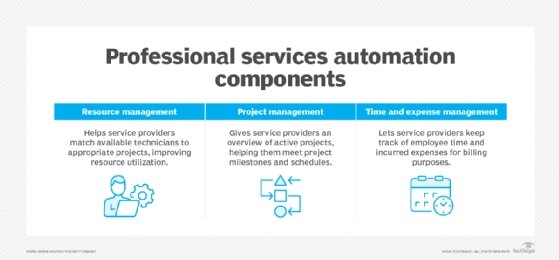
PSA tools encompass a range of functionality. Key components include project management, resource management, and time and expense management. The PSA category of software aims to help organizations meet project milestones and schedules; allocate resources to projects to optimize personnel use; and track employee time, billable hours and other expenses for billing purposes.
As a project begins, PSA tools identify and capture sales opportunities, guiding the process through pitching and resource allocation. As the project progresses, these systems facilitate the management of tasks and resources, ensuring that all elements align with the project's goals. The culmination of the project lifecycle includes invoicing, collecting payment and comprehensive reporting that provides critical insight into the project's performance and financial metrics.
Other PSA modules include customer relationship management, which keeps tabs on sales opportunities; help desk and service desk software; and reporting with dashboard capabilities.
Key features of PSA software
PSA software has several key features. The most important are the following:
- Project management. PSA software integrates various tools into a single platform to enhance project management. This centralization simplifies the management of project timelines, task allocation and progress monitoring, ensuring projects adhere to their schedules and budgets. By offering features like project setup, task management and deadline tracking, PSA tools aid in maintaining project structure and efficiency.
- Resource management. PSA tools provide detailed insights into personnel skills, availability and project suitability in ways that improve resource allocation. This facilitates effective workforce optimization and strategic planning for future resource needs. PSA resource management also includes time and expenses tracking, both of which support accurate billing and expense management.
- Financial management. PSA software offers functionalities for budgeting, financial forecasting and integration with existing account system workflows. This helps organizations control and improve their financial health. Project accounting and invoice management enable real-time insights and business intelligence into project budgets, profit margins and overall financial performance. All these capabilities help ensure projects remain profitable and financially viable.
Types of PSA software
PSA software can be implemented with on-premises products or with cloud-based services. Most PSA tools are cloud-based, with software as a service being a typical deployment model.
The cloud approach eases the hardware acquisition and management burden of an onsite offering. This is a plus for professional services firms looking to avoid onsite technology costs and focus on their core business lines. Cloud-based PSA tools also make it easier for companies to manage increasingly distributed and mobile workforces.
Professional services automation products use the level of integration they offer to differentiate themselves from other automation software and tools. Some PSA vendors offer integrated suites that combine PSA, remote monitoring and management (RMM), and remote-control software. PSA products offered as part of an integrated suite often integrate with third-party offerings. That way, a customer using a PSA product from one vendor can integrate that system with another vendor's RMM offering, for example.
Other vendors focus on PSA on its own without a broader suite of automation software products. However, the standalone PSA vendors often provide integrations with other applications, such as CRM and accounting.
Benefits of implementing PSA software
Implementing PSA software provides a number of benefits:
- Streamlined processes. PSA tools simplify and streamline several aspects of project management, including time tracking, expense reporting and invoicing, which enhance productivity and accuracy. Many PSA solutions also offer scalability, ensuring business processes continue to be effective as a business grows.
- Improved financial planning. PSA software supports budget management and financial forecasting by providing real-time insights into financial data. This integration allows for more accurate pricing and billing, improved cash flow and reduced billing disputes.
- Automation. As a key part of PSA tools, automation extends across functions such as accounting, invoicing, calendar management and billing. By automating repetitive tasks, PSA tools free employees to focus on higher-value activities that contribute to project success and client satisfaction.
- Real-time visibility. PSA software offers real-time insight into key performance indicators such as resource utilization, project profitability and revenue growth. This visibility contributes to effective project management and timely adjustments to resource allocation based on project demands and skill sets.
- Enhanced collaboration. PSA software centralizes all project-related data into a single platform, enhancing communication across teams. This centralization ensures that all team members have access to the same information, which enables better decision-making that helps services teams focus on the right projects and more efficient project execution.
Challenges of PSAs
There are several challenges associated with PSA software. The most important include the following:
- Complexity. Strategic implementation and implementing change management strategies are complicated processes, but they're crucial for integrating new technologies and other PSA-related tasks.
- Cost. Financial limitations can make investment in PSA tools daunting, particularly when dealing with high initial and other costs.
- Pace of change. The fast pace of digital transformation necessitates continuous technological updates, which can be challenging to adopt and train staff on.
Examples of PSA software
There are several PSA software options. Some of the examples based on TechTarget reporting and other market research companies, such as G2, include the following:
- BigTime.
- Certinia Professional Services Cloud.
- CloudBlue PSA.
- ConnectWise PSA.
- Datto Autotask PSA.
- Kantana Professional Services Cloud.
- Kaseya Business Management Solution.
- Keka PSA.
- NetSuite OpenAir.
- Rocketlane.
- SAP S/4HANA Cloud.
- Scoro.
- SuperOps.
Professional services automation software helps manage core business processes. Learn how to develop a business process.






