What is lead scoring?
Lead scoring is a methodology sales and marketing departments use to determine the worthiness of leads, or potential customers, by attaching values to them based on their behavior relating to their interest in products or services.
The value of each lead varies from company to company, but generally is characterized by the interest they show in the organization or their place in the buying cycle. Companies use point-based systems to qualify leads or simply refer to them as hot, warm or cold based on their history of interactions.
The first goal of companies is to get sales leads or prospects into their pipeline. Once a substantial number of leads has been obtained, it's important for companies to focus on the prospects that are most interested in buying, which is where lead scoring can play an important role.
Lead scoring helps marketing and sales teams identify where each potential customer is in the buying process and enables these teams to prioritize leads -- ideally increasing the rate at which they become customers.
The lead scoring process
Sales and marketing teams must agree on the definition of a qualified lead for the lead scoring process to begin. To score a lead, information is gathered about the lead's occupation and role in that industry to determine whether it's appropriate to sell to them. Information about a lead's activities, demographics or areas of interest is also important when determining whether that lead would be interested in a company's products or services.
Each action is assigned a point value depending on how likely the software predicts that action will lead to a purchase. Leads who are an ideal fit and have expressed a high interest in a company are rewarded with positive points, are deemed marketing-qualified leads and are typically passed to sales departments. Fewer points are awarded to those who are deemed a good fit but with minimal interaction. They might then be sent to marketing teams for lead nurturing. Points can also be subtracted from leads that show less interest. As an example, if a lead unsubscribes from an email list, then their score could be adjusted downward. These scores are continually updated to adjust for changes in behaviors over time.
To help measure a lead's level of interest in a product or service, organizations can track the following:
- Which email messages leads respond to.
- Which pages they visit on the company website.
- How long they look at the pages.
- If they filled out or downloaded any forms.
- Whether they clicked on a blog post or engaged on social media.
The importance of various metrics can change depending on whether the company is selling a product or service and what industry they're selling to. Likewise, the customer attributes chosen to define higher-quality leads change depending on the organization.
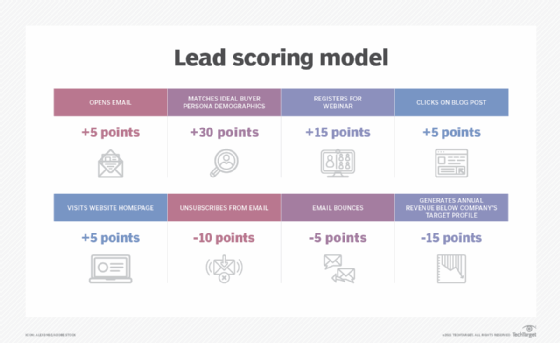
Before implementing lead scoring, organizations must first decide what the minimum criteria are for a lead to become a customer. They must also identify the characteristics of their target market, who their ideal leads are, what metrics and behaviors they will track and the lead scoring model they will use.
Why is lead scoring important?
Companies use historical data from processes such as marketing automation to predict a typical path that a customer takes before a sale is made. Using practices such as inbound marketing, marketing automation, customer data and lead nurturing, companies can examine which pieces of content are most engaging to customers and how many interactions between the organization and prospect it took to turn that person into a customer.
Lead scoring enables organizations to prioritize leads using an analytical approach, in what would normally be more of a subjective process. It's partly due to the lead scoring processes that enable sales teams to separate a customer's interest in products from their intent to buy. It's an important step in determining if a lead should continue to be nurtured and marketed to or handed over to sales teams.
For instance, website page views or downloads of certain documents might indicate that a prospect is merely interested but not intending to buy anything. These actions will be scored lower than customers who send buying signals by requesting a trial or viewing a pricing page.
If companies invest in lead scoring software to improve their overall sales process, it's important that marketing and sales teams closely align their lead management efforts. The technology must also be properly set up with the right metrics and should be used consistently. Otherwise, the lead scoring data could paint an incomplete picture of potential prospects, and take sales and marketing reps down a disadvantageous path.
Lead scoring metrics
Companies use various metrics to determine the success of lead scoring efforts. Sales teams should understand these metrics, which can vary from company to company, so they can optimize the effectiveness of their lead scoring systems.
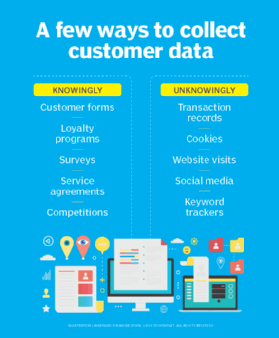
Lead scoring metrics can be broken down into two categories: demographic and behavioral. Demographic categories include the following:
- Location. The location of a lead determines their relevance, such as if the offered product or service is geographically or regionally dependent.
- Job title. The job title of a lead can determine their relevance to a product and can also indicate the lead's decision-making authority. A higher level of authority might receive a higher lead score.
- Industry. The industry the lead belongs to also helps to assess how relevant the lead is to an offered product or service.
- Company size. The size of the lead's company can indicate the lead's potential budget.
Behavioral metrics commonly include the following:
- Unsubscribe rates on emails. These rates measure the effectiveness of marketing campaigns and diagnose inaccurate targeting methods or flaws in the content. Conversely, response rates, or click-through rates -- the rate at which prospects open certain marketing materials or otherwise perform an intended action -- can measure the quality and effectiveness of the produced content.
- Lead engagement rate. Sales teams can compare lead scores -- or engagement scores -- of nurtured leads against those that haven't been touched by any sort of sales or marketing materials. This comparison lets them calculate the lead engagement rate. A drop in this metric signifies a need to update content or explore new channels of engagement. If companies focus content on guiding prospects to engage with the organization in a certain way, the lead engagement rate can show how effective certain types of content are.
- The source of information. Information sources that prospects use can indicate how interested they are in becoming a customer. For example, if they find content on a third-party site and click on it or download it, the prospect might be just gathering information on the software market. If the prospect exhibits buying signals by following or interacting with social media accounts, requesting trials or demos, or visiting pricing pages, they might gain a higher lead score.
- Social media interaction. Interactions on different social media platforms, such as likes, shares, favorites and saves can indicate interest levels.
- Demo requests. A request for a product demo or free trial indicates a higher level of interest. This action should be rewarded with a higher number of points.
- Purchase history. This is the signal of a repeat customer and can present the organization with more cross-selling opportunities.
- Sales cycle time. The sales cycle is the length of time it takes for a lead to become a customer. A shorter sales cycle indicates a more effective lead nurturing and scoring process.
- Upsell and cross-sell rates. Organizations can track how often sales teams successfully upsell and cross-sell products to leads. Lead scoring systems should value highly engaged leads who are well-versed in products because these leads are more likely to buy upgrades and additional products. A low upsell and cross-sell rate can indicate that an organization needs to adjust its lead scoring system to more strongly prioritize this type of customer.
Lead scoring models
A lead scoring model is a framework used to evaluate and rank potential leads. Numerical scores are assigned to leads in the model based on a set of defined criteria. The model also differs depending on the metrics being gathered. Example models include the following:
- Purchase intent model. This model is intended to help identify a lead's probability of conversion and how close they are to making a purchasing decision. For example, it would apply positive points to a lead requesting a quote or adding an item to a shopping cart.
- Demographic model. Also referred to as the firmographic model, this model is intended to identify leads that are close to the organization's target customer profile. Leads are scored based on demographic factors such as location, job title and company size.
- Online behavioral model. This model is intended to evaluate a lead's interest level based on their online activities. This can include their website visits, visiting pricing pages or filling out forms.
- Engagement models. This model is intended to evaluate a lead's interest level based on their level of engagement with an organization. Metrics scored include engagement on social media, participation in events or click-through rates on emails.
- Negative scoring. This is a model that's intended to subtract points based on behaviors or attributes that suggest a lead is less interested or engaged in a company, product or service. Negative points are assigned to leads that, for example, unsubscribe from emailing lists, are from a non-target industry, or are a student or someone unlikely to have purchasing authority.
Lead scoring tools
There are many software tools that can help companies implement lead scoring. Most large customer relationship management (CRM) vendors have some form of lead scoring tools. This includes products such as Adobe Campaign, Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Insights and Journeys, Oracle Marketing, Salesforce Einstein Lead Scoring and SAP Sales Cloud.
Beyond the large CRM vendors, several software companies also offer third-party lead scoring tools to plug into marketing and sales tools. According to Future Market Insights, this includes companies such as Bitrix24, Freshworks, Monday.com and Pipedrive.
Lead scoring tools help companies capture and nurture leads by monitoring their activity and then scoring it. When plugged into CRM systems and pipeline workflows, lead scoring tools can provide tremendous value by putting sales reps and marketers in front of the right prospect at the right time.
To help marketing and sales teams, lead scoring tools must do the following:
- Create and manage ranking scales for leads. Organizations should base these scales on their goals and market position. It would be detrimental for companies that focus on enterprise customers to nurture small and medium-sized customers as leads.
- Let users assign scores to leads. These tools should let sales agents score leads with their organization's predefined ranking system. If a company targets enterprises, its lead scoring system should score enterprise prospects higher than small businesses.
- Offer reporting and analytics features. These features can ensure leads align with what the company seeks in a customer.
- Integrate with external systems. Lead scoring tools should offer integrations with sales and marketing software, as well as analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) platforms. Many lead generation platforms have also begun integrating AI tools.
- Provide importing and exporting capabilities. These systems should let companies import data from other sources, such as surveys or industry statistics. Lead scoring results must be easy to export for use in reporting tools.
Lead scoring is an important part of the marketing and sales process in gauging lead interest. Learn more about lead scoring best practices that can improve the efficiency of sales.





